Fun with Data – Wafer Basics
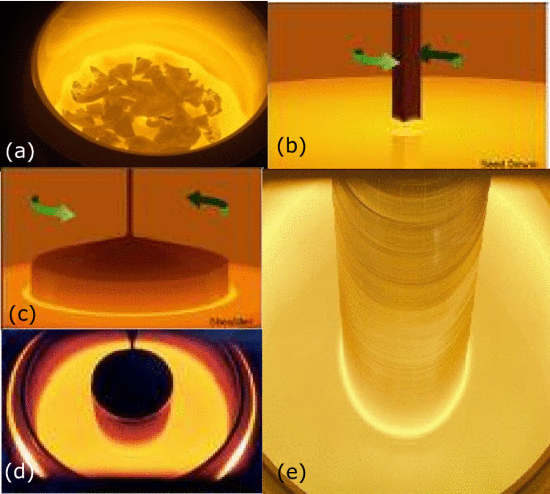
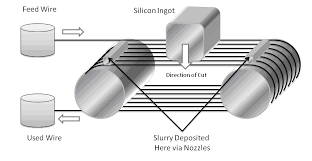
Silicon wafers are grown from metallurgical grade polysilicon, which is produced by mixing silica (Silicon Dioxide – SiO2) with Carbon and heating to 1,900⁰C in an arc furnace and is then converted to TCS (Trichlorosilane – SiHCl3), a liquid and further refined through distillation. The TCS is then converted to solid polysilicon through the Siemens process, and then reheated in a crucible (Czochralski Method). A seed crystal is dipped into the melt and is slowly pulled from the liquid as the silicon grows around the seed. By controlling the heat and ‘pull’ rate, the size of the silicon rod can be set.




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed