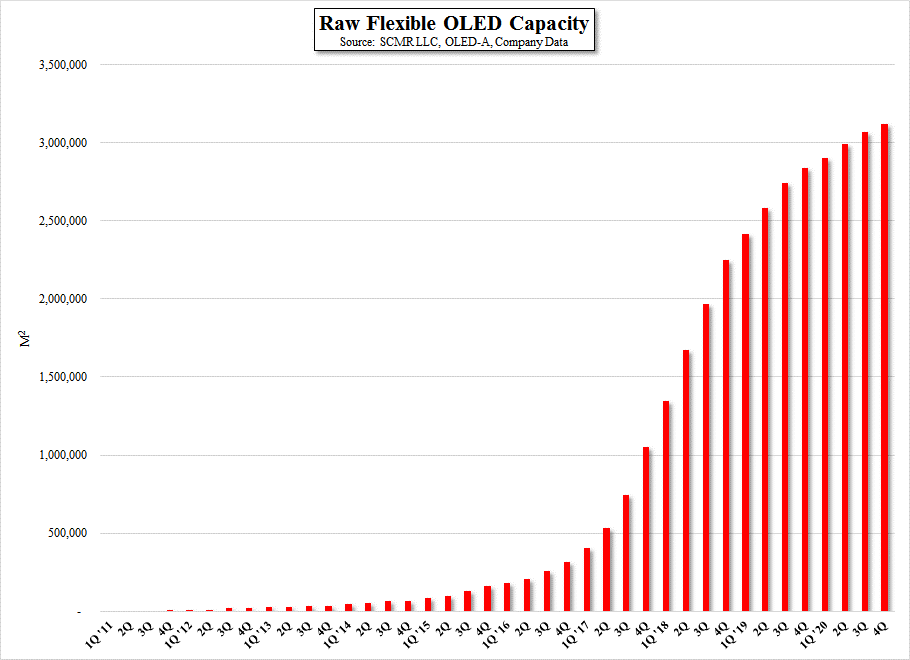
What is limiting flexible OLED growth?
Canon-Tokki (7751.JP) is the primary supplier of flexible OLED deposition equipment for large scale OLED display production, and while the company has announced plans to expand it production capabilities, it remains severely constrained as to production of this key OLED tool. We believe Canon is able to produce 7 high-volume tools this year, primarily Gen 6 size, but all of these are allocated to only three customers, with Samsung Display (pvt) receiving 5, and both LG Display (LPL) and BOE (200725.CH) each receiving one. With at least 8 new flexible OLED lines planned for this year, and a similar number planned for 2018, it will be difficult for all participants to meet flexible production timelines without deposition equipment. Of course, there are alternative manufacturers, but panel producers like to stay with what they know and what works, and the qualification process for such tools, given that they are the heart of the flexible OLED manufacturing process, is a long one, especially for those new to the space. Sunic (pvt), ULVAC (6728.JP), SFA (056190.KS), SNU (080000.KS) and Applied Materials (AMAT) all have OLED deposition tools, and have supplied OLED producers, but none have reached the level of Canon-Tokki, particularly with Samsung Display, the largest producer of small panel OLED displays, in terms of production capabilities. As they gain expertise and Canon-Tokki expands production, the deposition bottleneck will lessen, but we believe this is the biggest stumbling block to the progression of flexible OLED to the industry currently, and could last another year at least.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed